Fight Hyperpigmentation Through Diet: A Complete Guide on What Foods to Eat and Those to Avoid
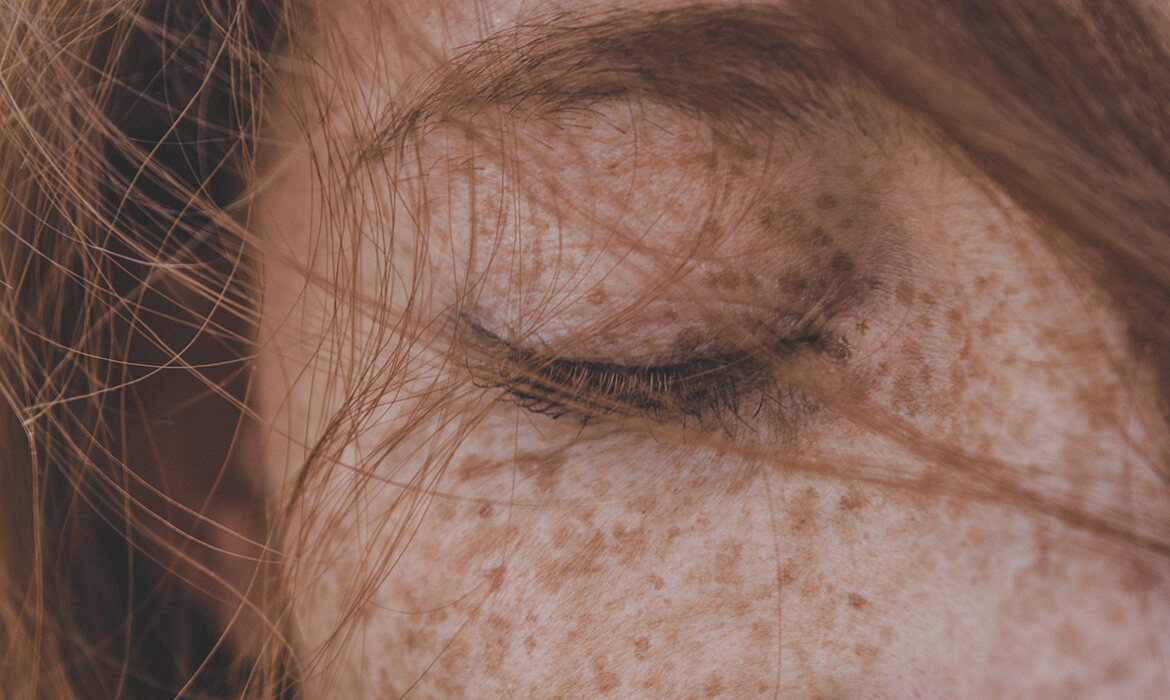
Hyperpigmentation is the term used to describe a skin condition where patches of skin become darker than its surrounding area due to an increase in melanin. Melanin is the pigment that gives your skin color. This skin condition is usually harmless and various factors can trigger its appearance.
Hyperpigmentation Causes and Triggers
Hyperpigmentation occurs due to an increase in melanin production. Some factors that may trigger excess melanin production include genetics, age, hormones, sun exposure, inflammation, and/or skin injuries.
Hyperpigmentation can be managed through diet by consuming foods that promote healing, reduce inflammation, and don’t provoke hormonal changes.
Foods to Incorporate These Into Your Diet
Your skin needs nutrients to renew and repair, so eating nutrient-dense foods is key if your goal is to achieve healthy skin. Foods rich in omega fatty acids, vitamins A + C, and minerals (zinc, calcium, magnesium, manganese) all play a vital role in maintaining an even skin tone.
Below are examples of foods to add to your diet and reasons why each of these is beneficial for your skin.
Avocados – antioxidant, fight free radical damage
Avocados are packed with healthy fats + help your body absorb fat soluble vitamins such as Vitamin A, which supports cellular growth.
Fatty Fish – Omega-3, anti-inflammatory
Fatty fish such as salmon are rich in Omega-3 fatty acids which help reduce inflammation in the body.
Sweet Potato, Carrots, Pumpkin – contain beta carotene
Vegetables that are vibrant orange in color contain a pigment called beta carotene. In the body, beta carotene gets converted to Vitamin A. Vitamin A is a potent antioxidant that scavenges free radicals and protects the skin against damage from the sun’s UV rays.
Citrus Fruits – antioxidant, contain Vitamin C
Citrus fruits like oranges, lemons, and limes contain high amounts of Vitamin C. Vitamin C promotes collagen production in the body and helps renew and repair the skin.
Dark Green Veggies (kale, broccoli, etc.) – contain Vitamin C + carotenoids
Dark green vegetables are high in antioxidants like Vitamin C. They also contain carotenoids which are precursors to Vitamin A. Carotenoids also filter out UV radiation and reduce oxidative stress in the skin.
Nuts and Seeds – contain healthy fats + minerals (zinc, magnesium, calcium, manganese)
Nuts and seeds are contain healthy Omega-3 fats and are rich in minerals that support skin healing and repair.
Foods to Limit or Avoid
Foods that should be limited or avoided altogether are ones that tend to cause inflammation in the body and/or may disrupt your hormone levels and create imbalances.
Dairy – contains synthetic hormones, inflammatory food
Dairy products such as milk often contain synthetic hormones passed down from the cows that were milked. These hormones get absorbed into your body and can alter or affect your hormonal levels.
Soy – contains phytoestrogen
Soy products contain phytoestrogen which mimic the estrogen in your body. This can disrupt your body’s own hormone levels.
Sugar – inflammatory food
Sugar is high on the glycemic index and is a top inflammatory food, which also means it can trigger skin hyperpigmentation. And if that wasn’t enough, sugar also breaks down collagen in the skin and causes premature aging. So it’s best to avoid it whenever possible!
Spicy and Fried Foods – inflammatory foods
Spicy foods and/or fried foods are also highly inflammatory in the body. Those foods should be limited as they can also trigger hyperpigmentation of the skin.
Caffeinated Drinks – trigger increase in cortisol hormone
Caffeine is another culprit for hormone imbalances. It can spike your cortisol levels and may alter estrogen levels. Reducing caffeinated drinks throughout the day is recommended if your skin is prone to hyperpigmentation.